Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
*;
JNC TN8400 2001-027, 131 Pages, 2001/11
In order to document a basic manual about input data, output data, execution of computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport calculation in heterogeneous porous rock, we investigated the theoretical background about geostastical computer codes and the user's manual for the computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport which calculates water flow in three dimension, the path of moving radionuclide, and one dimensional radionuclide migration. In this report, based on above investigation we describe the geostastical background about simulating heterogeneous permeability field. And we describe construction of files, input and output data, a example of calculating of the programs which simulates heterogeneous permeability field, and calculates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Therefore, we can document a manual by investigating the theoretical background about geostastical computer codes and the user's manual for the computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport calculation. And we can model heterogeneous porous rock and analyze groundwater flow and radionuclide transport by utilizing the information from this report.
Tamura, Kazuo*; Iriya, Yoshikazu*
JNC TJ9440 2000-004, 22 Pages, 2000/03
In the probabilistic safety assessment(PSA), the fault tree/event tree technique has been widely used to evaluate accident sequence frequencies. However, event tansition which operators actually face can not be dynamically treated by the conventional technique. Therefore, we have made the dynamic analysis program(DYANA) for event transition for a liquid metal cooled fast breeder reactor. In the previous development, we made basic model for analysis. However, we have a probrem that calculation time is too long. At the current term, we made parallelization of DYANA usig MPI. So we got good performance on WS claster. It performance is close to ideal one.
*; *
JNC TJ9440 2000-002, 90 Pages, 2000/03
In order to support development of the dynamic reliability analysis program DYANA, analyses were made on the event sequences anticipated under emergency situations using the plant dynamics simulation computer code Super-COPD. In this work 9 sequences were analyzed and integrated into an input file for preparing the functions for DYANA using the analytical model and input data which developed for Super-COPD in the previous work. These sequences could not analyze in the previous work, which were categorized into the PLOHS (Protected Loss of Heat Sink) event.
Koga, Jiro*; Shinzato, Takushi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-054, 48 Pages, 2000/02
The "STELLA" which is a tool for simulation of dynamical systems applied to the numerical simulation of the behavior of minor constituent, such as hydrazoic acid, forming and extinguishing on the operation of reprocessing process. The concentration of hydrazoic acid forming by the reaction of nitrite and hydrazine were determined by use of STELLA after the determination of concentration of main constituents by MIXSET-X. The results from simulation is shown that the STELLA is applicable to the numerical simulation of the behavior of minor constituent.
Yamada, Susumu*
JNC TJ8400 2000-051, 122 Pages, 2000/02
Developing an inexpensive on-line criticality surveillance system is required for ensuring the safety of nuclear fuel reprocessing plants. Based on the series of researches for five years, R&D study on On-line Criticality Surveillance System has been carricd out since 1996. The concept of this Criticality Surveillance System is based on the Auto-Regressive Moving Average (ARMA) model identification algorithms to the time series of signal fluctuation of a neutron detector. We have proposed several new ideas of modification to the original design of the Criticality Surveillance System, and also reported some results of numerical analysis over the DCA experiments. In those days, DOS/V personal computers with Microsoft Windows have came into wide use instead of those based on the MS-DOS, which have been popular in Japan. NEC, a major maker of MS-DOS computers, stopped the production of MS-DOS computers and changed their management policy toward production of DOS/V personal computers. Our researches have been developed using MS-DOS computers. For the effective use of these important results, it became an urgent theme to transplant all programs developed on MS_DOS computers into computers with the OS, which is not easily affected by commercialism. Since the design concept should be based on high reliability, electromagnetic disturbance-free and high expandability, and also computers have achieved remarkably high performance as well as low price in these days, these computers should be used not only as a simple signal processing unit but also a totally integrated signal analyzing system along with conventional signal analyzing software in stead of IC chips with analyzing soft wares. This configuration enables us to easily introduce newly developed techniques and to provide supplement information. Then, this approach can enhance the reliability of the Criticality Surveillance System without addition of any special devices, and also provide the flexibility of ...
Ohno, Shuji; Matsuki, Takuo*; ; Miyake, Osamu
JNC TN9520 2000-001, 196 Pages, 2000/01
ASSCOPS (Analysis of Simultaneous Sodium Combustion in Pool and Spray) has been developed for analyses of thermal consequences of sodium leak and fire accidents in LMFBRs. This report presents a description of the computational models, input and output data as the user's manual of ASSCOPS version 2.1. ASSCOPS is an integrated computational code based on the sodium pool fire code SOFIRE II developed by the Atomics International Division of Rockwell International, and on the sodium spray fire code SPRAY developed by the Hanford Engineering Development Laboratory in the U.S. The users of ASSCOPS need to specify the sodium leak conditions (leak flow rate and temperature, etc.), the cell geometries (cell volume, surface area and thickness of structures, etc.), and the atmospheric initial conditions such as gas temperature, pressure, and composition. ASSCOPS calculates the time histories of atmospheric temperature, pressure and of structural temperature.
Nakagawa, Tsuneo
JAERI-Data/Code 99-041, p.98 - 0, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Tsuneo; Katakura, Junichi; *
JAERI-Data/Code 99-032, 65 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Tsuneo; *; Fukahori, Tokio
JAERI-Data/Code 99-030, 81 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
*; Nakagawa, Tsuneo; *
JAERI-Data/Code 99-025, 46 Pages, 1999/04
no abstracts in English
PNC TN9410 98-007, 93 Pages, 1998/02
This report presents numeical results on thermal striping charactelistics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm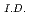 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V
elbow and a branch pipe having same inner diameter to the main pipe, and five velocity ratio conditions between both the pipes, i,e., (V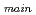 / V
/ V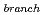 ) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.
) = 0.25; 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 and 4.0. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)Temperature fluctuations in the downstream region of the tee junction were formulated by lower frequency components (< 7.0Hz) due to the iteractions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe, and higher frequency components (> 10.0 Hz) generated by the vortex released frequency from the outer edge of the branch pipe jet flows. (2)On the top plane of the main pipe, peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was decreased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe, and its position was shifted to downstream direction of the main pipe by the increase of the main pipe flow velocity. (3)On the bottom plane of the main pipe, contrary to (2), peak values of the temperature fluctuation amplitude was increased with increasing flow velocity in the main pipe.
Hunter
PNC TN9460 98-001, 156 Pages, 1998/01
This document provides a description of a calculational route, used in the Reactor Physics Research Section for sensitivity studies and initial design optimization calculations for fast reactor cores. The main purpose in producing this document was to provide a description of and user guides to the calculational methods, in English, as an aid to any future user of the calculational route who is (like the author) handicapped by a lack of literacy in Japanese. The document also provides for all users a compilation of information on the various parts of the calculational route, all in a single reference. In using the calculational route (to model Pu burning reactors) the author identified a number of areas where an improvement in the modelling of the standard calculational route was warranted - the document includes a description of these changes. The calculational route makes use of several different computer programs. SLAROM calculates nuclear data from compositions, using either homogeneous or heterogeneous models. CITATION and MOSES do reactor burn-up and/or flux diffusion calculations; CITATION is used for 2D (RZ) calculations, whilst MOSES models 3D (hex-Z) geometry. PENCIL and CITDENS are essentially specialized versions of CITATION (PENCIL includes data preparation and other functions). MASSN calculates fuel cycle mass balances. PERKY performs perturbation and associated calculations, both 1'st order and exact perturbations. JOINT and RZOUT3 provide various dataset interface functions, including energy group condensation. Briefer descriptions of the calculational route are given, followed by a more detailed step-by-step approach to the calculations. This latter includes examples of all JCL and data files, and a description of all the data that a user may have to employ. The document does not give a complete description of the component programs: where options and/or data are not used in any of the calculations they have generally been ignored; ...
; Ohno, Shuji; Miyake, Osamu; ; Seino, Hiroshi
PNC TN9520 97-001, 185 Pages, 1997/12
ASSCOPS(Analysis of Simultaneous Sodium Combustion in Pool and Spray) has been developed for analyses of thermal consequences of sodium leak and fire accidents in LMFBRs. This report presents a description of the computational models, input, and output as the user's manual of ASSCOPS version 2.0. ASSCOPS is an integrated code based on the sodium pool fire code SOFIRE II developed by the Atomics International Division of Rockwell International, and the sodium spray fire code SPRAY developed by the Hanford Engineering Development Laboratoly in the U.S. The experimental studies conducted at PNC have been reflected in the ASSCOPS improvement. The users of ASSCOPS need to specify the sodium leak conditions (leak flow rate and temperature, etc.), the cell geometries (volume and structure surface area and thickness, etc.), and the atmospheric initial conditions, such as gas temperature, pressure, and gas composition. ASSCOPS calculates the time histories of atmospheric pressure and temperature changes along with those of the structural temperatures.
; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
PNC TN9410 97-104, 69 Pages, 1997/12
As the part of the improvement of single-phase subchannel analysis code ASFRE-III, verification study about fuel-pin heat transfer model and flow resistance model of the code was carried out. Temperature distributions in a fuel pin predicted by the fuel-pin heat transfer model of ASFRE-III were compared with those calculated by the structure analysis code FINAS, which has been well validated and applied to various structure analyses, using the same boundary conditions. The comparison showed that the results by these two codes agreed with maximum difference of 1 %. and therefore the validity of the model was confirmed. With respect to the flow resistance model, distributed resistance model (DRM), which can enhance the consistent description of the fluid flow and wire-spacer interaction, was examined through analyses of two hydraulic simulation tests using the fifth mock-up fuel subassembly for the prototype LMFBR and the second mock-up fuel subassembly for the experimental rector. The calculated pressure difference between pressure measurement taps whose positions were near the top and the bottom of the fuel-pin bundle agreed with the measured data of both tests. The predicted pressure distribution in a horizontal cross section was also compared with the calculational result by the finite element analysis code SPIRAL and agreement was good.
Nakagawa, Tsuneo; Watanabe, Takashi*; *
JAERI-Data/Code 97-050, 103 Pages, 1997/12
no abstracts in English